We have recognized two genes from Arabidopsis that present excessive similarity with CBF1, a gene encoding an AP2 domain-containing transcriptional activator that binds to the low-temperature-responsive factor CCGAC and induces the expression of some cold-regulated genes, rising plant freezing tolerance.
These two genes, which we’ve got named CBF2 and CBF3, additionally encode proteins containing AP2 DNA-binding motifs. Furthermore, like CBF1, CBF2 and CBF3 proteins additionally embody putative nuclear-localization indicators and potential acidic activation domains.
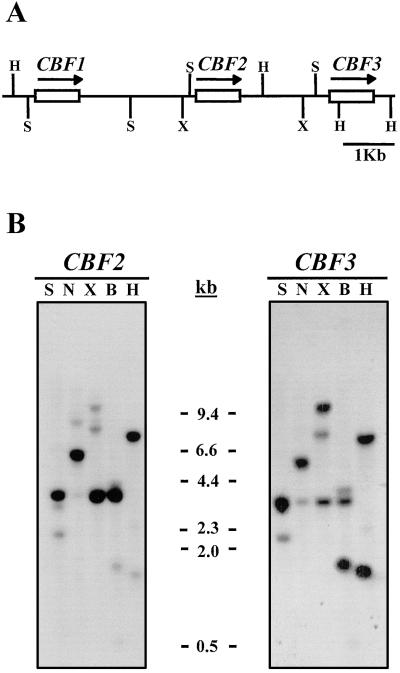
The CBF2 and CBF3 genes are linked to CBF1, constituting a cluster on the underside arm of chromosome IV.
The excessive stage of similarity among the many three CBF genes, their tandem group, and the truth that they’ve the identical transcriptional orientation all recommend a standard origin. CBF1, CBF2, and CBF3 present equivalent expression patterns, being induced very quickly by low-temperature therapy.
However, in distinction to most of the cold-induced plant genes characterised, they’re not attentive to abscisic acid or dehydration. Taken collectively, all of these knowledge recommend that CBF2 and CBF3 might perform as transcriptional activators, controlling the extent of low-temperature gene expression and selling freezing tolerance by way of an abscisic acid-independent pathway.
The Caenorhabditis elegans gene unc-89, required fpr muscle M-line meeting, encodes a large modular protein composed of Ig and sign transduction domains.
Mutations within the Caenorhabditis elegans gene unc-89 end in nematodes having disorganized muscle construction by which thick filaments are not organized into A-bands, and there are not any M-lines. Beginning with a partial cDNA from the C. elegans sequencing challenge, we’ve got cloned and sequenced the unc-89 gene.
An unc-89 allele, st515, was discovered to comprise an 84-bp deletion and a 10-bp duplication, leading to an in-frame cease codon inside predicted unc-89 coding sequence.
Analysis of the whole coding sequence for unc-89 predicts a novel 6,632 amino acid polypeptide consisting of sequence motifs which have been implicated in protein-protein interactions. UNC-89 begins with 67 residues of distinctive sequences, SH3, dbl/CDC24, and PH domains, 7 immunoglobulins (Ig) domains, a putative KSP-containing multiphosphorylation area, and ends with 46 Ig domains.
A polyclonal antiserum raised to a portion of unc-89 encoded sequence reacts to a twitchin-sized polypeptide from wild sort, but truncated polypeptides from st515 and from the amber allele e2338. By immunofluorescent microscopy, this antiserum localizes to the center of A-bands, per UNC-89 being a structural part of the M-line.
Previous research point out that myofilament lattice meeting begins with positional cues laid down within the basement membrane and muscle cell membrane. We suggest that the intracellular protein UNC-89 responds to those indicators, localizes, after which participates in assembling an M-line.
